Project Profile
Mitigating Blast Load Hazards on Metal Buildings
Explore our Extreme Loads and Structural Risk modeling capabilities to address complex facility siting hazards, including mitigating the risk of structural failure from potentially catastrophic events.
Project Objectives

#1
Develop retrofit design of a pre-engineered metal building subject to blast loads from a vapor cloud explosion
#2
Apply numerical modeling expertise and our high performance computing (HPC) system to solve complex behavior of the frame
#3
Optimize design of structural system to reduce overall cost and mitigate the risk of structural failure
Project Overview
A facility siting study was performed for a major petrochemical company in compliance with the United States Department of Labor's standard for process safety management of highly hazardous chemicals (OSHA 29 CFR 1910.119), and using the guidance outlined in the American Petroleum Institute's Recommended Practice 752. The outcome from this study indicated unacceptable building damage from the modeling of an extreme load event, such as vapor cloud explosions.
We developed an optimized design compliant with structural performance criteria and a cost-efficient retrofit solution.
ABS Group's Extreme Loads and Structural Risk (ELSR) division provides a full spectrum of engineering services to assist in the evaluation and design of remediation for fire, explosion and toxic hazards as part of facility siting. The solution in this particular case involved using finite element analysis (FEA) to better evaluate the building frame's structural response and subsequent repair recommendations. Our predictive modeling capabilities help reduce both risk and construction costs while also delivering more resilient designs that can withstand extreme load conditions.
Client Needs
- Determine specific weaknesses in the existing building frame system using both local and global failure modeling
- Apply FEA to design blast retrofits for the pre-engineered metal building frames
- Deliver an optimized design that complies with structural performance criteria and minimizes capital expenditures
- Minimize business interruption and construction time
Our Solution
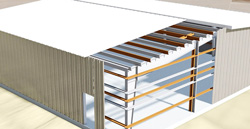
Typically, pre-engineered metal building (PEMB) frames are optimized for code-based wind loading and possess little reserve capacity for forces from extreme loading events. In particular, analysis of the building showed that the moment frames, among other structural components, were insufficient to resist the extreme load event in accordance with established acceptance criteria.
An FEA was used to develop retrofit strategies that 1) were effective in achieving the desired building response and 2) optimized the additional steel (weight/cost) and construction complexity (schedule/cost). An FEA models structural response well into the plastic range and can capture local failure modes which conventional design codes and traditional dynamic methods do not model.
Using the FEA, we evaluated the building frame's structural response and repair, eliminating conservatisms in simpler failure models. Coupled with a more robust explicit dynamic solver and a fully customizable structural system, we were able to more accurately replicate the response up to, and including, structural failure.
In this case scenario, our ELSR team provided detailed modeling services to address complex facility siting hazards. This included applying computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling to develop refined loading (from explosion and thermal loading), blower door testing to quantify building leakage rates for toxic and flash fire concerns, site-wide mitigation plan development and remediation planning, multi-hazard building design, new building blast/structural design, retrofit blast/structural design, cost estimation, construction support and the development of corporate standards.
Our ability to provide support and counsel through the complete cycle of the facility siting process—from screening evaluation of hazards through remediation—provides our clientele with a more holistic solution.
Figures and video demonstrate modeling capabilities for analyzing and optimizing structural designs.